Aquí os dejo un link superbueno, un diccionario visual en inglés, sólo necesitais tener paciencia y ganas de aprender.
¡Espero que os guste!
http://visual.merriam-webster.com/
viernes, 25 de diciembre de 2009
TOOLS
viernes, 12 de junio de 2009
lunes, 8 de junio de 2009
Electricity links
CIRCUIT SYMBOLS of electric components:
http://www.kpsec.freeuk.com/symbol.htm
ELECTRICITY AND THE ELECTRON:
http://www.kpsec.freeuk.com/electron.htm
CIRCUIT DIAGRAMS:
http://www.kpsec.freeuk.com/cdiags.htm
http://www.kpsec.freeuk.com/symbol.htm
ELECTRICITY AND THE ELECTRON:
http://www.kpsec.freeuk.com/electron.htm
CIRCUIT DIAGRAMS:
http://www.kpsec.freeuk.com/cdiags.htm
jueves, 4 de junio de 2009
martes, 2 de junio de 2009
Insulators and Conductors
A. Classify each material as a Conductor or as a Insulator. Translate into Spanish
plastic dirty water
aluminium silver
copper paper
wood silk
glass clay
iron concrete
rubber bronze
gold steel
cotton cement
B. Fill in the blanks with the words in the box below:
insulators electric field ions attract electric current negatively conductors electric charge repel positively
1. The two types of _____________________________ are positive and negative. Like charges _________________________ and unlike charges _________________________ each other.
2. An object becomes _____________________________ charged if it gains electrons and _______________________ charged if it loses electrons.
3. Electrically charged objects have an __________________________ surrounding them and exert electric forces on each other.
4. ________________________ is the flow of charges, usually electrons or _____________________.
5. Electrons can move easily in __________________________, but not so easily in _________________________.
plastic dirty water
aluminium silver
copper paper
wood silk
glass clay
iron concrete
rubber bronze
gold steel
cotton cement
B. Fill in the blanks with the words in the box below:
insulators electric field ions attract electric current negatively conductors electric charge repel positively
1. The two types of _____________________________ are positive and negative. Like charges _________________________ and unlike charges _________________________ each other.
2. An object becomes _____________________________ charged if it gains electrons and _______________________ charged if it loses electrons.
3. Electrically charged objects have an __________________________ surrounding them and exert electric forces on each other.
4. ________________________ is the flow of charges, usually electrons or _____________________.
5. Electrons can move easily in __________________________, but not so easily in _________________________.
Electricity Exercises
1. Answer the following questions:
1. What is electric current?
2. What units are used to measure current?
3. Which materials allow current to flow easily?
4. Which materials prevent the flow of electric current?
5. Write five examples of conductor materials and five of insulator materials.
6. What is the symbol of a battery, a cell, a resistance, a lamp, a fuse, a switch, a motor?
7. What units are used to measure resistance and voltage?
8. What symbols are used to represent current, potential difference (voltage), and resistance?
1. What is electric current?
2. What units are used to measure current?
3. Which materials allow current to flow easily?
4. Which materials prevent the flow of electric current?
5. Write five examples of conductor materials and five of insulator materials.
6. What is the symbol of a battery, a cell, a resistance, a lamp, a fuse, a switch, a motor?
7. What units are used to measure resistance and voltage?
8. What symbols are used to represent current, potential difference (voltage), and resistance?
Electricity
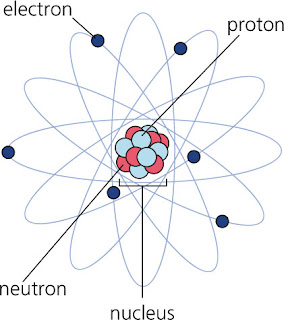 1. INTRODUCTION
1. INTRODUCTIONMatter is made up of very tiny particles called atoms. ATOMS are the smallest particles of an element that have the same chemical properties as the element itself.
Nowadays we know that the atom is not indivisible, but it is made up of smaller particles called protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons and neutrons are in the nucleus. Electrons move around the nucleus. Protons have a positive electric charge, neutrons are neutral and electrons are negatively charged. An atom has equal number of protons and electrons.
2. INSULATORS AND CONDUCTORS.
Electric charges move more easily through conductors than through insulators.
A material in which electrons can’t move easily from place to place is called an insulator (plastic, wood, glass, rubber).
Materials that are conductors contain electrons that can move more easily in the material (copper, gold, aluminium, iron).
3. VOLTAGE, CURRENT AND RESISTANCE
The flow of charge is called the current and it is the rate at which electric charges pass though a conductor. The charged particle can be either positive or negative.
In order for a charge to flow, it needs a push (a force) and it is supplied by Voltage (V), or potential difference. The charge flows from high potential energy to low potential energy. The unit is Volt (V).
The Current (I) measures the amount of charge that passes a given point every second. The unit for current is Ampere (A).
Resistance (R) is a feature of a material that determines the flow of electric charge. The unit of resistance is Ohm (Ω ). The resistance varies in different materials. For example, gold, silver, and copper have low resistance, which means that current can flow easily through these materials. Glass, plastics, and wood have very high resistance, which means that current can not pass throught these materials easily.
A German scientist Georg Simon Ohm experimented with circuits and found out the relationships between current, voltage, and resistance. It became known as Ohm's law and can be written in an equation V=IR, where V is voltage, I is current, and R is resistance.
One terminal of a cell or battery is positive, while the other is negative. It is convenient to think of current as flowing from positive to negative. This is called conventional current
A cell provides a steady voltage, so that current flow is always in the same direction. This is called direct current, or d.c. . This gives rise to alternating current, or a.c., in which the charge carriers move backwards and forwards in the circuit.
A cell provides a steady voltage, so that current flow is always in the same direction. This is called direct current, or d.c. . This gives rise to alternating current, or a.c., in which the charge carriers move backwards and forwards in the circuit.
4. OHM´S LAW
The relationship between current, voltage and resistance was discovered by Georg Ohm. He made his own wires and was able to show that the size of an electric current depended
 upon their length and thickness. The current was reduced by increasing the length of the wire, or by making it thinner. Current was increased if a shorter thicker wire was used.
upon their length and thickness. The current was reduced by increasing the length of the wire, or by making it thinner. Current was increased if a shorter thicker wire was used.sábado, 30 de mayo de 2009
World Environment Day
Hi friends,
Commemorated yearly on 5 June, WED is one of the principal vehicles through which the United Nations stimulates worldwide awareness of the environment and enhances political attention and action.
Click in this link http://www.eia.doe.gov/kids/ and you´ll have fun energy activities with Energy Ant!
Good luck!!
Commemorated yearly on 5 June, WED is one of the principal vehicles through which the United Nations stimulates worldwide awareness of the environment and enhances political attention and action.
Click in this link http://www.eia.doe.gov/kids/ and you´ll have fun energy activities with Energy Ant!
Good luck!!
jueves, 7 de mayo de 2009
Exercise- Computers
Departamento de Tecnología Unit 8. Computers
Name: Group: Date: Mark:
1.Complete the following definitions:
1. A ______________________is a programmable machine.
2. A _________________________is a tool that is used for typing like a typewriter
3. A ____________________is the screen on your computer that you look at.
4. A ____________________is piece of plastic that has a ball on the bottom and two buttons on the top.
5. A ____________________is a machine that puts things from the computer onto paper.
6. The part that lets you hear the sounds from the programs is called ________________
2. What do the following abbreviations mean?
1. CPU:
2. RAM:
3. ROM:
3. Translate into English:
a. Ratón b. Pantalla c. Monitor
d. Impresora e. Escaner f. Teclado
g. Auriculares h. Micrófono i. Altavoz
j. Disquete k. Disco duro l. Placa base
Name: Group: Date: Mark:
1.Complete the following definitions:
1. A ______________________is a programmable machine.
2. A _________________________is a tool that is used for typing like a typewriter
3. A ____________________is the screen on your computer that you look at.
4. A ____________________is piece of plastic that has a ball on the bottom and two buttons on the top.
5. A ____________________is a machine that puts things from the computer onto paper.
6. The part that lets you hear the sounds from the programs is called ________________
2. What do the following abbreviations mean?
1. CPU:
2. RAM:
3. ROM:
3. Translate into English:
a. Ratón b. Pantalla c. Monitor
d. Impresora e. Escaner f. Teclado
g. Auriculares h. Micrófono i. Altavoz
j. Disquete k. Disco duro l. Placa base
Computer- Links
http://www.abcya.com/computer_vocabulary.htm
Parts of a computer- DEFINITIONS
DEFINITIONS
Computer- Technically, a computer is a programmable machine. This means it can execute a programmed list of instructions and respond to new instructions that it is given.
Floppy Disk- a disk is a piece of plastic that holds information for or from your computer.
C.D.-a round circle holds information for or from your computer.
BD. Blue- Ray Disk-.is an optical disc format such as CD or DVD. While a CD can hold 700 MB of data and a basic DVD can hold 4.7 GB of data, a single Blu-ray disc can hold up to 25 GB of data.
DVD- DVD, also known as "Digital Versatile Disc" or "Digital Video Disc," is an optical disc storage media format. Its main uses are video and data storage.
Hard Disk Drive-the hard drives are machines that have a lot of memory to save your work and carries a c.d.rom and a floppy disk.
Keyboard-a keyboard is a tool that is used for typing like a typewriter.
Monitor- a monitor is the screen on your computer that you look at when you are on the computer
Mouse- A piece of plastic that has a ball on the bottom and two buttons on the top. When you click on the mouse, you usually click on the left button.
Printer- A machine that puts things from the computer onto paper.
Scanner- A piece of equipment that copies pictures so that you can use it in your computer projects.
Speakers- The part of the computer that lets you hear the sounds from the programs.
Modem- A part of the computer that connects to the phone lines so that you can go on the Internet.
Motherboard- A main board of the computer that has many chips on it. The motherboard makes the computer work. It also is where the memory and the processing are found.
Chip- A small piece inside the computer that helps your computer work. Chips have to be programmed by people or they won't work. There are many chips in a computer.
CPU (Central Processing Unit)- A chip that is the "brain" of your computer that processes the information.
Virus- A software that damages your computer system.
World Wide Web- A part of the internet that let's you jump from site to site alot quicker.
RAM (Random Access Memory)- Memory chips in the computer that hold information to run your programs.
ROM (Read Only Memory)- A permanent memory chip that cannot be changed. This memory runs the computer.
Bit- A small piece of information that gives directions to the computer.
Byte- A byte is also information that gives the computer directions. A byte contains eight bits.
Software- The programs that run on the computer.
Hardware- The physical parts of the computer.
Suscribirse a:
Entradas (Atom)






























